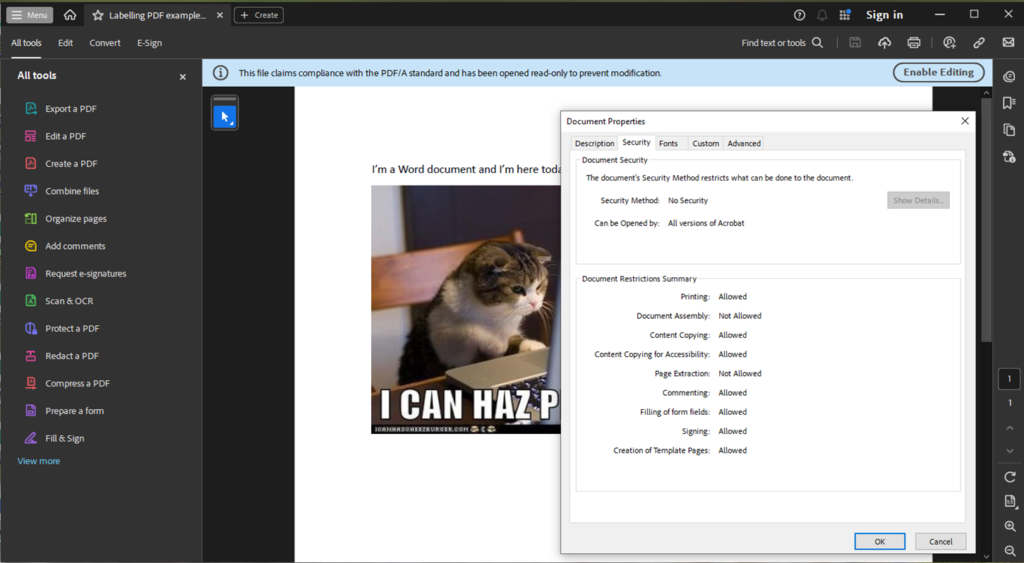
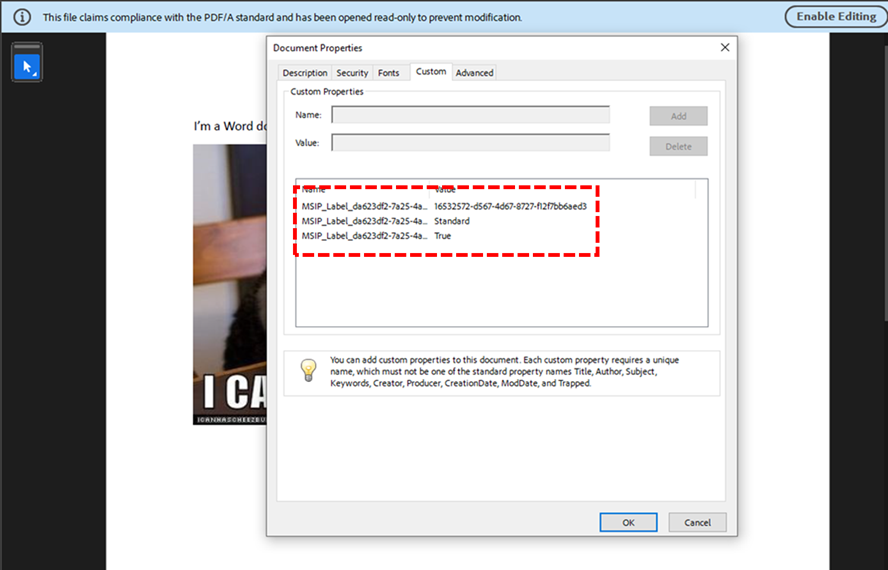
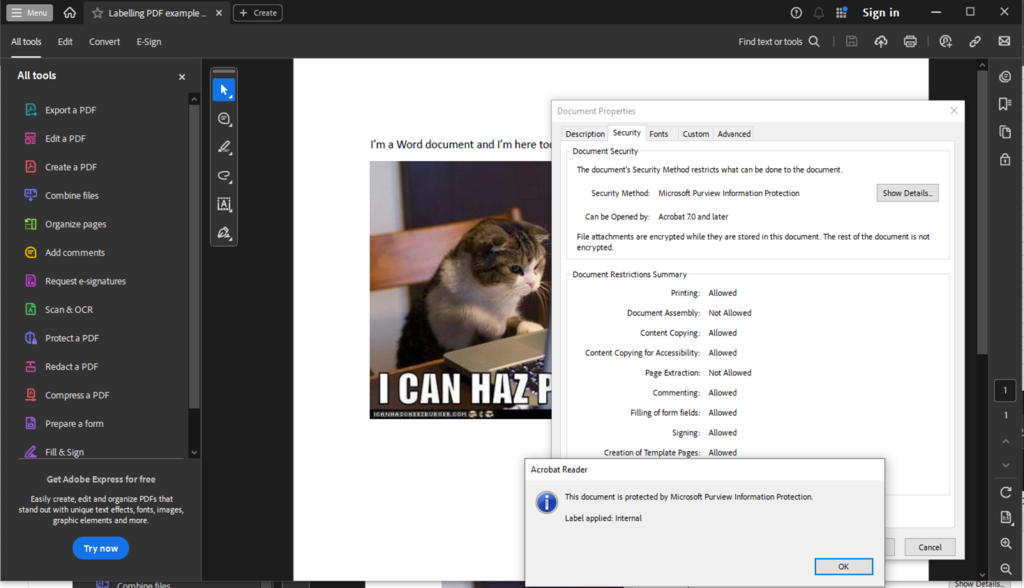
Congratulations, CISO! 🎉 Great job in landing your new role, where protecting sensitive data isn’t just a job—it’s a daily tightrope walk over a pit of cyber threats, compliance demands, and evolving technology.

Now that you’re at the steering wheel, your inbox is probably overflowing with security concerns, regulatory requirements, and a few “fun” audit emails. Don’t worry, you’re in good company. This guide is here to give you actionable steps to set up your Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategy, ensuring you don’t just survive in this role—you thrive.
So, what does being a CISO mean? Well, you’re now the go-to person when sensitive data sneaks out, malicious insiders get a bit too curious, or someone clicks that suspicious link promising free money from an unknown relative in Timbuktu. No pressure, right? But here’s the deal: inaction is risk. Delaying or overlooking the core elements of a solid DLP strategy could lead to breaches that cost more than your next cybersecurity budget.
To make your journey smoother, I’ve prepared a handy worksheet that you can use right now to take action on your Data Loss Prevention strategy. These aren’t just checkboxes—these are critical steps to lock down your organization’s data and avoid waking up to a breach nightmare.
You can Download the worksheet below.
Here’s what you can expect see inside:
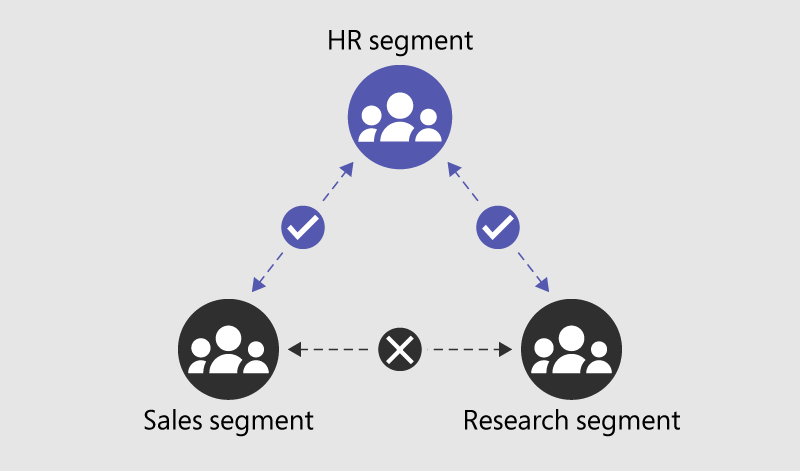
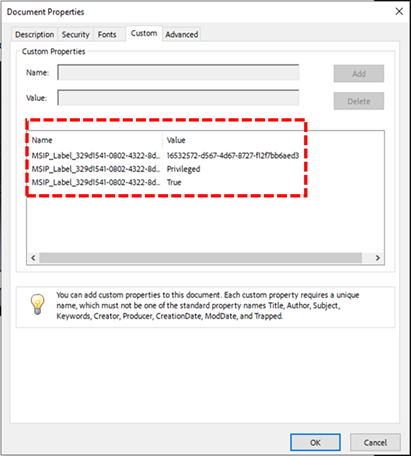
1. Classifying Data and Why It’s Important
Why it matters: Not all data is created equal. By classifying your data, you can prioritize resources and security measures where they’re needed most. Would you protect the company picnic plan with the same force as your customers’ financial information? (Spoiler: probably not!)
Example:
- High-risk data: Customer credit card details, proprietary code, or confidential HR files—things you’d never want to see in the wrong hands.
- Medium-risk data: Internal meeting notes, marketing strategies—sensitive, but not catastrophic if leaked.
- Low-risk data: Public reports, customer FAQs—this is the stuff you’d share at a conference.
Take Action Today: Review your organization’s data and start tagging it by risk level. Ask yourself, “What would happen if this data got out?” and use that to guide your classification efforts
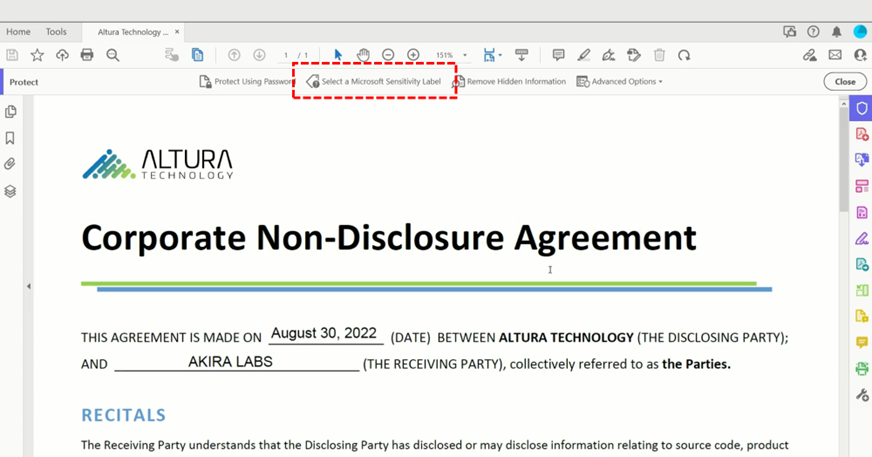
2. Why and How to Identify Sensitive Data
Why it matters: You can’t protect what you don’t know exists. Sensitive data is often hidden across different platforms—sometimes even in the most unexpected places (like a random email attachment or NTFS file shares). Identifying it is the first step to ensuring it stays secure.
Example:
- Sensitive Data: Personally Identifiable Information (PII) like social security numbers or health records, intellectual property (IP), and anything that’s subject to regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Surprise Discovery: Finding a list of client emails attached to a forgotten project buried in a shared folder.
Take Action Today: Use a discovery tool or audit your data manually. Start with cloud storage, email servers, and shared folders. Look for data that could lead to a privacy violation or financial loss if exposed.

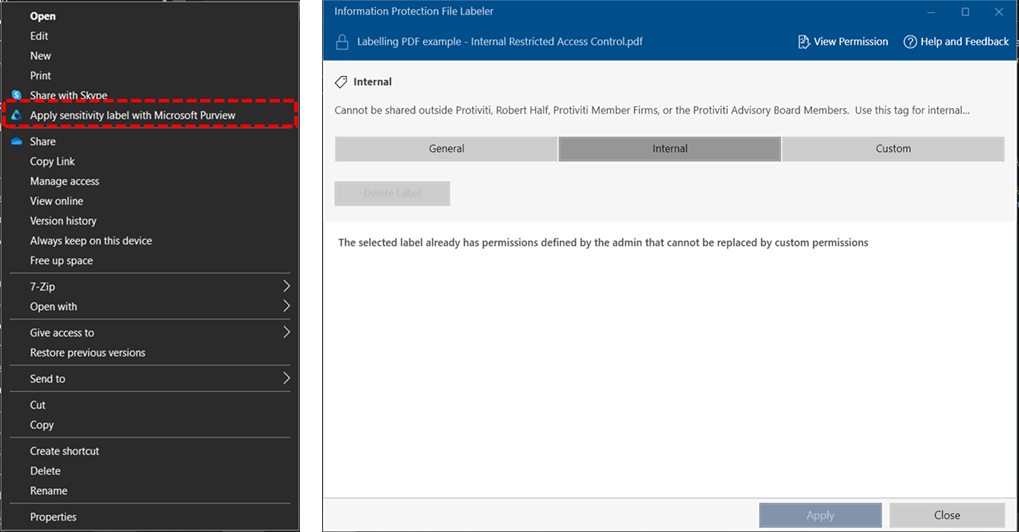
3. Developing a Data Handling Policy
Why it matters: A solid data handling policy is the foundation of your DLP strategy. Without clear rules in place, sensitive information can slip through the cracks, exposing your organization to unnecessary risk. Your data handling policy ensures everyone—from top execs to interns—understands the dos and don’ts of handling sensitive information.
Example:
- Clear Guidelines: For high-risk data like financial information, the policy might mandate encryption during transfer and restricted access to authorized personnel only.
- Real-Life Scenario: Imagine your marketing team accidentally sharing a file with customer details over an unsecured network. A proper data handling policy would prevent this by enforcing secure file transfer practices.
Take Action Today: Draft a policy that covers how different types of data (high, medium, low risk) should be handled. It should specify everything from encryption requirements to access control and data retention periods. Involve key stakeholders (Legal, IT, HR) to ensure all bases are covered.
Now that you know the key steps to securing your organization’s data, it’s time to plan it out, partner with your internal stakeholders, and take action. DLP isn’t a one-person job—it’s a team effort that involves collaboration across IT, Legal, HR, and beyond. The risks of inaction are far too high, so don’t wait until something goes wrong. Proactively implementing these best practices today will not only protect your data but also strengthen your leadership as a new CISO.